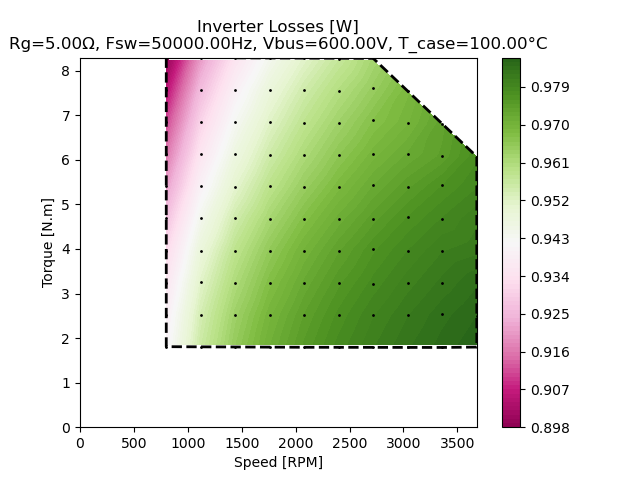
Efficiency map of a motor drive inverter
Download Python Library requirements
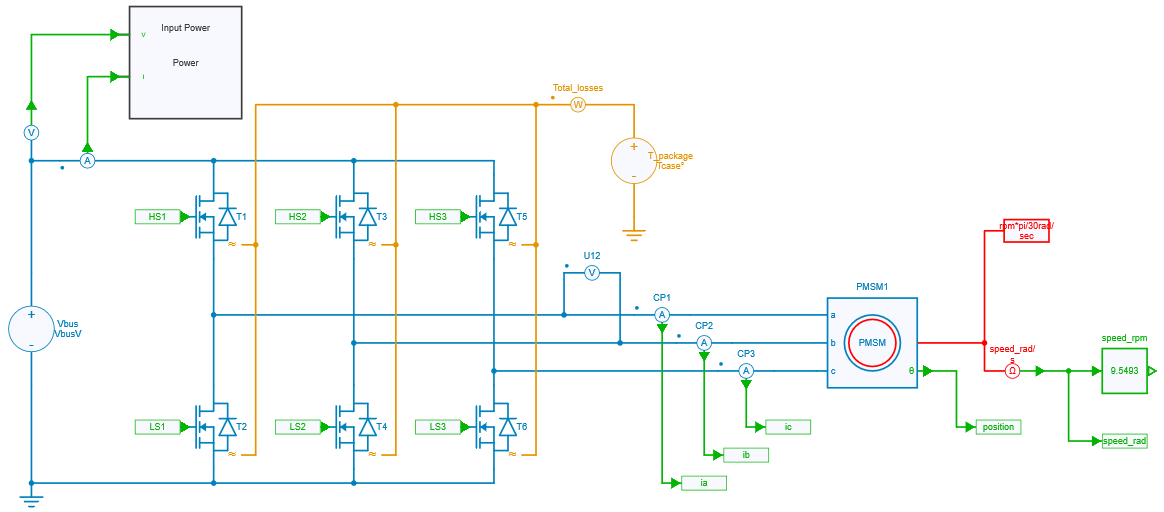
Motor drive inverter model
Inverter & motor model in SIMBA
The motor drive inverter model consists of a 3-phase 2-level voltage source inverter (VSI) that supplies a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM). The PMSM is connected to a load that imposes a constant speed, meaning that the motor must be able to produce enough torque to maintain the desired speed.
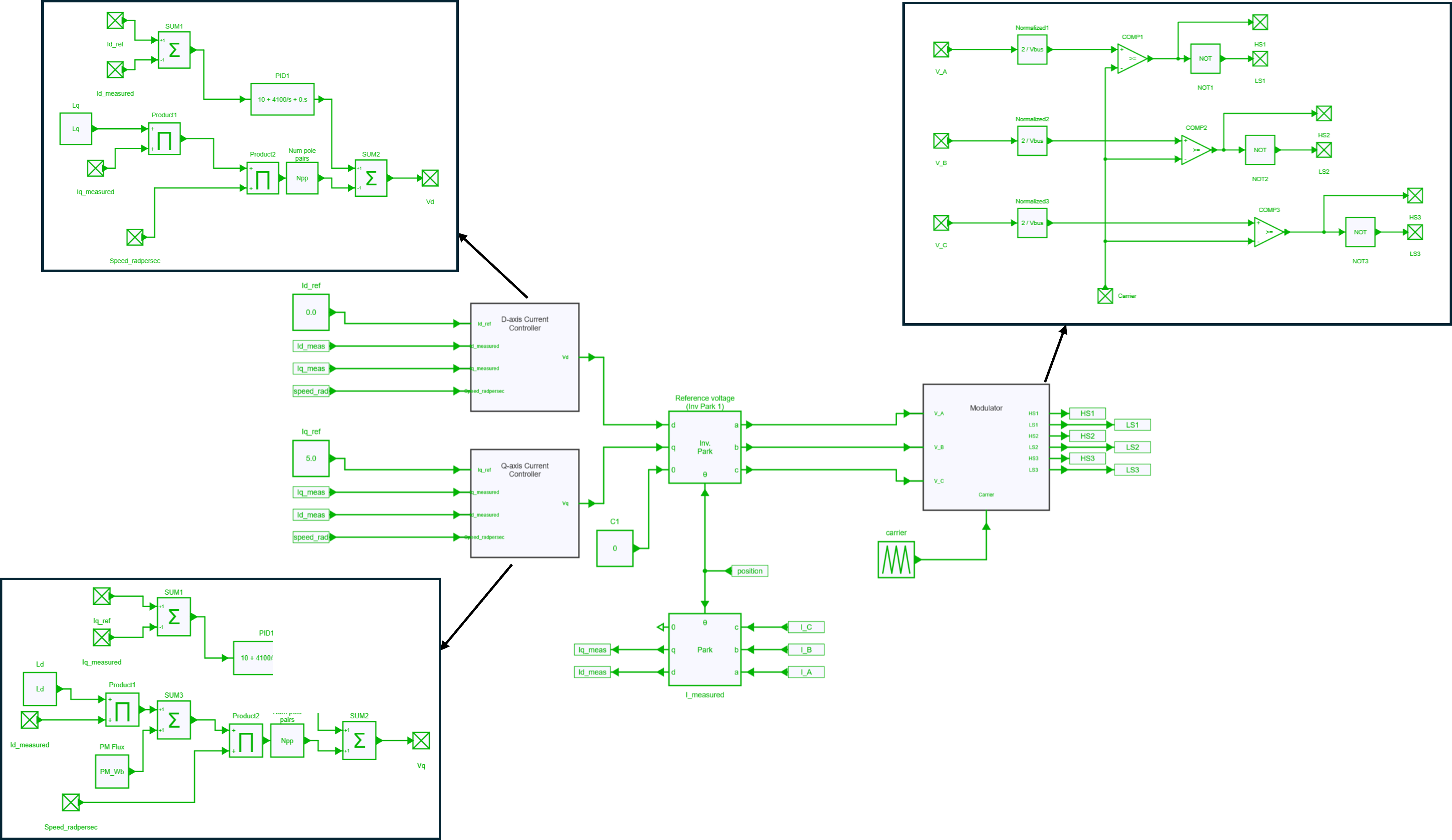
Control
PMSMs have a strong coupling between the d- and q-axis currents, so a decoupling network is required to linearise and remove the coupling effect. The control system consists of two PI controllers and a decoupling network. The calculated reference voltages are fed into the sinusoidal PWM modulator to generate voltage signals for the motor windings. The duty cycle of the PWM signal determines the magnitude of the voltage applied to the motor.
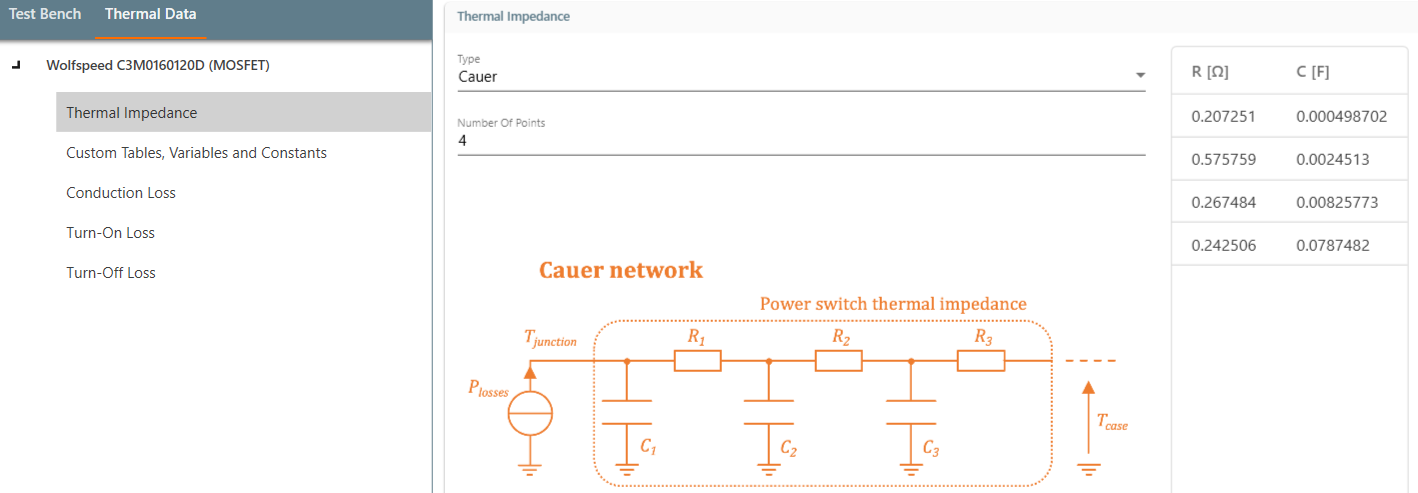
Thermal modeling
To model the thermal performance of MOSFETs in an inverter, their package temperature is held constant and data is extracted from the .xml files provided by the manufacturer. This data, which includes parameters such as thermal impedance, conduction losses and switching losses, plays a crucial role in determining the power dissipation during operation. In this particular case, Wolfspeed C3M0160120D transistors were used.
Python script
This script uses the architecture presented in the tutorial Parallel (multiprocessing) computing and also available on Github repository).
Its primary objective is to run simulations at various operating points, such as different torque and speed levels, to obtain power switch losses in steady-state and generate an efficiency map of the inverter. To achieve this, the script uses the multiprocessing library in Python, which allows multiple simulations to be run in parallel, increasing simulation speed and efficiency.
import multiprocessing
from tqdm import tqdm
number_of_parallel_simulations = License.NumberOfAvailableParallelSimulationLicense()
Id, Iq current references calculation
Current references are calculated using MTPA (Maximum Torque Per Ampere) and FW (Flux Weakening) algorithm according to the targeted operation point. The function SelectIdIq() takes in current and speed references, and returns a boolean value indicating whether the Id and Iq references were successfully calculated or not.
Operating points
The efficiency of the motor is calculated with the use of function run_simulation() for each current and speed reference defined as:
speed_refs = numpy.arange(min_speed_ref, max_speed_ref, (max_speed_ref - min_speed_ref)/number_of_speed_points)
current_refs = numpy.arange(min_current_ref, max_current_ref, (max_current_ref - min_current_ref)/number_of_current_points)
max_speed_ref and max_current_ref variables.
Multiprocessing
The code creates a multiprocessing manager and a dictionary calledresult_dict that will be used to store the results of the simulation.
for current_ref in current_refs:
for speed_ref in speed_refs:
ref_idiq = [0.0, 0.0]
ret = SelectIdIq(ref_idiq, current_ref, speed_ref)
if ret == True:
pool_args.append((ref_idiq[0], ref_idiq[1], speed_ref, case_temperature, Rg, i, result_dict, lock));
i=i+1
SelectIdIq() function to get the desired current reference values. The computed values are added to the pool_args if the function returns True.
pool = multiprocessing.Pool(number_of_parallel_simulations)
for _ in tqdm(pool.imap(run_simulation_star, pool_args), total=len(pool_args)):
pass
Note
The variable named "number_of_parallel_simulations" allows to set automatically the number of available parallel simulation based on the license of each user. This variable is defined earlier into the python script directly.
The code creates a processing pool using multiprocessing.Pool(number_of_parallel_simulations) and starts the simulation using pool.imap(run_simulation_star, pool_args). The tqdm() function is used to display a progress bar for the simulation.
for i in result_dict.items():
t.append(i[1][1])
s.append(i[1][2])
e.append(i[1][3])
t = numpy.array(t)
s = numpy.array(s)
e = numpy.array(e)
show_heatmap(s, t, e)
result_dict, stores them in arrays t, s, e and uses them to create a heatmap plot using the show_heatmap() function.
Results
The efficiency map was generated for a total of 100 speed / torque targets using the following simulation parameters:
ccase_temperature = 100 # Case temperature [Celsius]
Rg = 5 # Gate resistance [Ohm]
switching_frequency = 50000; # Switching Frequency [Hz]
bus_voltage = 600.0; # Bus Voltage [V]
max_speed_ref = 4000 # RPM
max_current_ref = 15.0 # A
number_of_speed_points = 10 # Total number of simulations is number_of_speed_points * number_of_current_points
number_of_current_points = 10 # Total number of simulations is number_of_speed_points * number_of_current_points
relative_minimum_speed = 0.2 # fraction of max_speed_ref
relative_minimum_current = 0.2 # fraction of max_torque_ref
simulation_time = 0.4 # time simulated in each run
NPP = 5.0; # PMSM Number of pole pair
PM_Wb = 0.0802; # PMSM Ke/NPP
Ld_H = 14.0e-3; # Motor Ld [H]
Lq_H = 14.0e-3; # Motor Ld [H]
Rs = 0.814 # Motor Stator Resistance [Ohm]

The resulting efficiency map of the PMSM inverter, is shown below: