Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine (PMSM)
Description
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine (PMSM)
Model of a three-phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine (PMSM) with the sinusoidal back Electro-Motive Force (EMF). In motor operation torque and speed have the same sign. Rotor Angle is defined as the angle between the a-phase and the d-axis. In this model, the saturation can be modeled using a piecewise linear approximation of direct and quadratic axis inductances. Stator winding is star connected in this model. To access the neutral point pin, check the "Neutral Point" checkbox in the properties menu.
Electrical model and equations
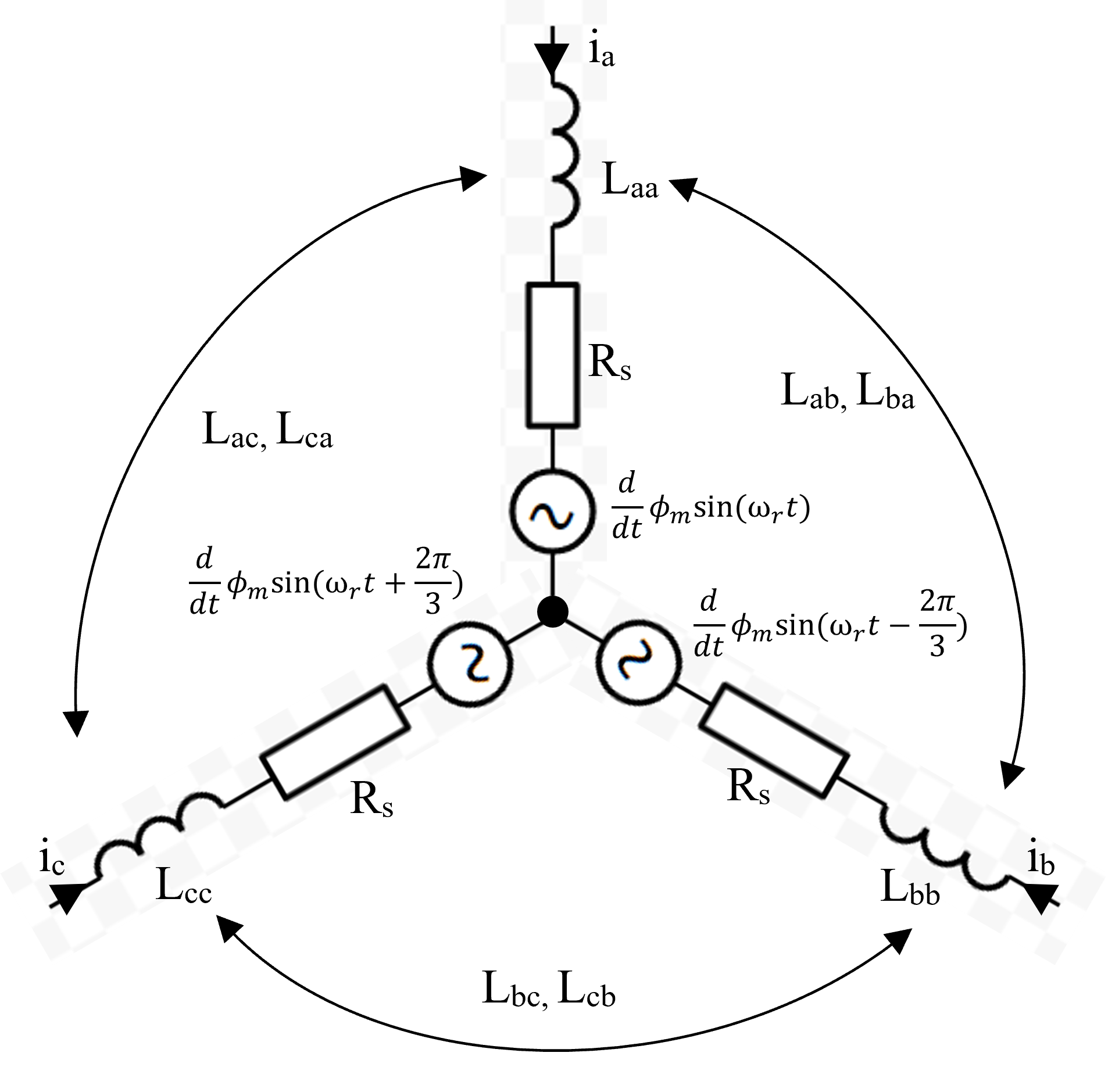
where \phi_m = \frac{K_e}{ N_{ pp} } is the permanent magnet flux linkage, and \omega_r = N_{pp} \Omega is the electrical speed of the rotor field.
Phase inductances (L_{aa}, L_{ab}, L_{ac},..., L_{cc}) are calculated from the rotor reference frame inductance (L_{d}, L_{q}) defined in the property panel as the incremental inductance.
This component will use the lineary interpolated inductance when the current is between the two segmented points.
Electromechanical equations
Electro-magnetic torque:
where \phi_d = L_d i_d + \phi_m and \phi_q = L_q i_q
Mechanical rotational speed \Omega:
Library
Electrical > Motors
Pins
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Pin_A | Phase A (Electrical) |
| Pin_B | Phase B (Electrical) |
| Pin_C | Phase C (Electrical) |
| Pin_R | Rotor (Rotational Mechanical) |
| Pin_Angle | Rotor Angle in radians, electrical angle (Control) |
| Pin_N | Neutral Point (Electrical) |
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Rs | Stator Winding Resistance [Ohm] |
| Ld | Direct Axis Inductance [H] |
| Lq | Quadratic Axis Inductance [H] |
| Ke | Back-EMF Constant |
| J | Rotor Inertia [kg.m²] |
| B | Rotor Friction Coefficient [N.m/(rad/s)] |
| InitialSpeed | Rotor initial speed [ rad/s] |
| NPP | Number of pole pairs |
| ExposeNeutralPoint | Neutral Point |